As a seasoned DevOps/SRE/DevSecOps/AIOps/MLOps/DataOps/FinOps career mentor and technical writer, I have helped countless engineers and managers navigate the complex landscape of modern software delivery practices. One certification that stands out in the field of DevOps is the Certified DevOps Professional (CDP). This comprehensive guide will provide you with everything you need to know about this certification and how it can propel your career forward.
What is the Certified DevOps Professional Certification?
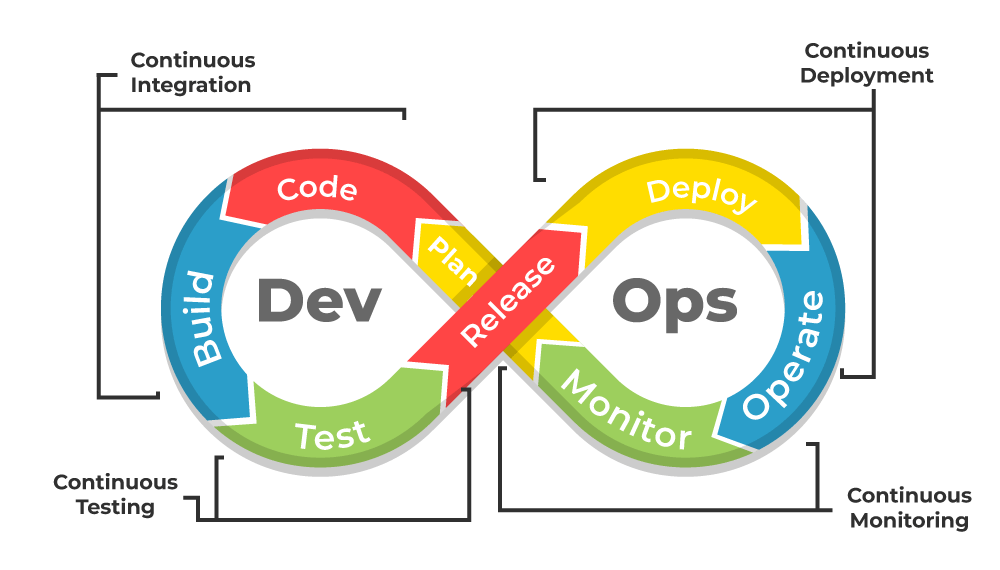
The Certified DevOps Professional (CDP) certification is an advanced-level credential that validates your expertise in the core principles of DevOps, continuous integration, continuous delivery (CI/CD), infrastructure as code (IaC), cloud computing, automation, and monitoring. This certification demonstrates your ability to streamline and automate processes across development and operations teams, ensuring higher quality and faster delivery of software. It is designed for professionals looking to deepen their DevOps knowledge and skills in complex, large-scale environments. Earning the CDP certification signals your proficiency in designing and managing efficient DevOps workflows and methodologies.
Who Should Take the Certified DevOps Professional Certification?
The Certified DevOps Professional (CDP) certification is ideal for professionals with some experience in DevOps, software engineering, or IT operations who want to level up their skills. It is best suited for:
- DevOps Engineers: Professionals looking to formalize their DevOps knowledge and gain deeper insights into automating workflows and managing DevOps pipelines.
- Site Reliability Engineers (SRE): Individuals focusing on maintaining reliable and scalable systems while implementing DevOps practices.
- Platform Engineers: Engineers responsible for maintaining the infrastructure that supports development and operations environments.
- Cloud Engineers: Professionals who are involved in managing cloud-based environments and want to integrate DevOps practices for improved scalability and efficiency.
- Software Engineers: Developers who aim to adopt DevOps practices for streamlined coding, testing, and deployment.
- Engineering Managers: Leaders who wish to guide their teams in adopting DevOps principles for better collaboration and faster delivery.
The CDP certification is recommended for individuals with prior experience or knowledge of DevOps and CI/CD concepts, as it builds on foundational skills.ns.
Skills You’ll Gain
By earning the Certified DevOps Professional certification, you’ll gain the following skills:
- Infrastructure as Code (IaC): Understanding the automation of infrastructure provisioning using tools like Terraform and Ansible.
- CI/CD Implementation: Mastery of Continuous Integration and Continuous Delivery pipelines, utilizing tools like Jenkins, GitLab CI, and CircleCI.
- Monitoring & Logging: Expertise in monitoring the health of infrastructure and applications with tools like Prometheus, Grafana, and ELK stack.
- Cloud Computing: Proficiency in using AWS, Azure, or GCP to manage scalable infrastructure.
- Automation & Orchestration: Deep knowledge of automating system operations and deployments.
- Security Practices: Embedding security into the DevOps pipeline (DevSecOps) to ensure secure, reliable software delivery.
Real-World Projects You Should Be Able to Do After It
After achieving the Certified DevOps Professional certification, you should be capable of handling several real-world projects, including:
- Automating CI/CD Pipelines: Designing and implementing fully automated CI/CD pipelines using popular tools like Jenkins, GitLab CI, CircleCI, or Bamboo to streamline testing and deployment workflows.
- Infrastructure as Code (IaC): Using tools like Terraform, Ansible, or AWS CloudFormation to automate infrastructure provisioning, configuration, and management.
- Cloud Infrastructure Management: Setting up scalable, cost-effective cloud environments using AWS, Azure, or GCP, including automation of resource management and deployment.
- Monitoring & Incident Response: Implementing monitoring systems with tools such as Prometheus, Grafana, or the ELK stack, allowing for quick incident detection and resolution.
- Security Automation (DevSecOps): Integrating security scans and controls into CI/CD pipelines to ensure software is secure at every stage of the delivery process.
- Containerization & Orchestration: Utilizing Docker and Kubernetes to containerize applications and manage their deployment in production environments.
These projects reflect the skills learned during the certification process and demonstrate how to integrate DevOps practices into real-world IT workflows.
Preparation Plan
To ensure success in the Certified DevOps Professional exam, follow this structured preparation plan:
7-14 Days Plan:
- Day 1-3: Brush up on the fundamentals of DevOps and key tools (CI/CD, Docker, Jenkins, Terraform).
- Day 4-7: Dive deep into IaC tools and automation practices (focus on Terraform, Ansible, and Kubernetes).
- Day 8-10: Study cloud services (AWS, Azure, GCP) and container orchestration (Kubernetes).
- Day 11-14: Review security practices and best practices for implementing them in a DevOps pipeline.
30 Days Plan:
- Week 1: Learn about CI/CD and Infrastructure Automation.
- Week 2: Deep dive into containerization and orchestration (Docker, Kubernetes).
- Week 3: Focus on Cloud services and monitoring.
- Week 4: Practice real-world projects and review your knowledge by taking practice tests.
60 Days Plan:
- Weeks 1-2: Learn and practice advanced CI/CD tools, Docker, and Terraform.
- Weeks 3-4: Study cloud architecture and cost management.
- Weeks 5-6: Practice real-world deployment scenarios, automated security testing, and application monitoring.
Common Mistakes to Avoid
When pursuing the Certified DevOps Professional certification and applying DevOps principles in your work, avoid these common mistakes:
- Neglecting the Basics: Skipping the foundational concepts such as version control, basic scripting, or the principles of Agile and Scrum can result in gaps in knowledge. Ensure you have a solid understanding of these fundamentals before diving into advanced topics.
- Overlooking Security (DevSecOps): Security is an integral part of DevOps, but many professionals fail to integrate security into their CI/CD pipeline, leaving vulnerabilities. Make sure security practices are embedded throughout the development and deployment process.
- Relying Too Much on Tools: While tools like Jenkins, Docker, or Kubernetes are essential, understanding the principles behind these tools is just as important. Avoid tool-centric thinking; focus on the principles of automation, collaboration, and continuous improvement.
- Skipping Hands-On Practice: DevOps is about practice and real-world experience. It’s easy to focus on theoretical knowledge, but practical application is where the true learning happens. Engage in projects or hands-on labs to reinforce your learning.
- Ignoring Soft Skills: DevOps isn’t just about technology—it’s about collaboration and communication between teams. Neglecting soft skills such as communication, teamwork, and problem-solving can hinder your success in a DevOps role.
Best Next Certification After CDP
After completing the Certified DevOps Professional certification, consider these next steps:
- Same Track: Certified DevOps Architect (CDA) – Take your skills further by learning about designing enterprise-scale DevOps solutions.
- Cross-Track: Certified Kubernetes Administrator (CKA) – Gain deeper expertise in container orchestration and cluster management.
- Leadership: Certified DevOps Leader (CDL) – Move into leadership roles by mastering the management of DevOps teams and processes.
Choose Your Path
After completing the Certified DevOps Professional certification, you can choose from several career paths depending on your interests and aspirations:
- DevOps: Focus on automating and improving the software development lifecycle, handling CI/CD, and maintaining infrastructure.
- DevSecOps: Specialize in integrating security practices into DevOps pipelines, ensuring that applications are secure from the start.
- Site Reliability Engineering (SRE): Concentrate on maintaining scalable, reliable systems while ensuring a smooth integration between development and operations.
- AIOps/MLOps: Explore automation in the realm of artificial intelligence and machine learning, focusing on system monitoring and management.
- DataOps: Focus on managing data pipelines, ensuring smooth integration between development, data management, and operational systems.
- FinOps: Bridge the gap between finance and technology by focusing on optimizing cloud costs and ensuring financial accountability in cloud environments.
Each path provides opportunities to specialize in different aspects of DevOps, and selecting the right one depends on your interests and career goals.
Role → Recommended Certifications
| Role | Recommended Certifications |
|---|---|
| DevOps Engineer | Certified DevOps Professional (CDP), Certified DevOps Architect (CDA) |
| SRE | Certified Site Reliability Engineer (CSRE), Certified DevOps Professional (CDP) |
| Platform Engineer | Certified DevOps Professional (CDP), Certified Kubernetes Administrator (CKA) |
| Cloud Engineer | AWS Certified Solutions Architect, Google Cloud Professional Architect |
| Security Engineer | Certified Information Systems Security Professional (CISSP), DevSecOps Professional |
| Data Engineer | Google Cloud Professional Data Engineer, Certified DataOps Professional |
| FinOps Practitioner | FinOps Certified Practitioner, AWS Certified Cloud Practitioner |
| Engineering Manager | Certified DevOps Leader (CDL), Certified ScrumMaster (CSM) |
FAQs (12 Questions & Answers)
- How difficult is the Certified DevOps Professional certification?
The exam is challenging but manageable with proper preparation. It requires a solid understanding of DevOps principles, cloud computing, CI/CD, and infrastructure automation. - How much time should I spend preparing for the CDP exam?
Depending on your background, preparation could take anywhere from 30 to 60 days. Aim to practice hands-on skills alongside theoretical learning. - Do I need any prerequisites for the Certified DevOps Professional exam?
Yes, some experience with DevOps tools and practices is recommended. Familiarity with cloud platforms and automation tools will be beneficial. - What’s the recommended sequence of certifications?
Start with foundational certifications like Certified DevOps Engineer, then progress to more advanced certifications like CDP, followed by specialized tracks such as DevSecOps or Kubernetes. - What career outcomes can I expect after earning the CDP certification?
With a CDP certification, you’ll be well-positioned for roles such as DevOps Engineer, SRE, Cloud Architect, and Engineering Manager. It opens up numerous opportunities in automation, cloud computing, and CI/CD. - How much does the Certified DevOps Professional exam cost?
The exam fee is usually around $500–$700. The cost may vary depending on the provider and your location. - How long is the CDP certification valid for?
The certification is valid for 2-3 years. After that, you can recertify by taking a refresher exam. - Can I take the exam remotely?
Yes, many certification providers offer remote proctored exams, allowing you to take the test from the comfort of your home or office. - What is the pass percentage for the Certified DevOps Professional exam?
The pass percentage for this exam typically ranges between 70% and 80%. - Are there any recommended study materials for the exam?
Yes, DevOps School offers official study guides and online courses that cover all exam objectives in depth. - Can I take practice exams before attempting the real exam?
Yes, practice exams are available to help you familiarize yourself with the exam format and assess your readiness. - What happens if I fail the exam?
You can retake the exam after a waiting period. Many providers offer discounts for retakes or allow you to review your weak areas before attempting again.
Top Training & Certification Providers
Here are some institutions that offer training and certification for the Certified DevOps Professional:
- DevOpsSchool: Provides in-depth courses on DevOps principles, tools, and techniques with hands-on labs.
- Cotocus: Specializes in delivering high-quality DevOps training, including certification exam preparation.
- SCMGalaxy: Known for offering expert-led courses in DevOps and Agile methodologies.
- BestDevOps: Offers personalized coaching and certification prep for DevOps professionals.
- DevSecOpsSchool: Provides specialized training on integrating security within DevOps pipelines.
- SRESchool: Focuses on training and certifications for Site Reliability Engineers, combining DevOps and reliability best practices.
- AIOpSchool: Offers training on AIOps and MLOps, helping professionals apply AI/ML in DevOps environments.
- DataOpSchool: Focuses on DataOps and the integration of data management with DevOps processes.
- FinOpSchool: Provides comprehensive training in FinOps for cloud cost optimization.
The Certified DevOps Professional (CDP) certification is an excellent step for professionals looking to advance their careers in the fast-evolving world of DevOps. It equips you with critical skills in automation, cloud computing, CI/CD, security, and infrastructure management. With this certification, you demonstrate your ability to deliver high-quality software efficiently and securely, which is highly valued in today’s competitive job market.
By carefully selecting your learning path and gaining hands-on experience, you can use the CDP certification as a stepping stone toward higher-level roles in DevOps, such as DevOps Architect, Site Reliability Engineer, or even leadership positions like DevOps Manager. As the demand for DevOps skills continues to grow, obtaining this certification can significantly enhance your career prospects and open the door to exciting job opportunities across industries.
Let this guide serve as your roadmap to becoming a Certified DevOps Professional, and take the next step toward mastering one of the most in-demand skills in the IT industry.